Why Rotational Molding?
Many people may have this problem in their minds. This technical article tells us in details about it including rotomolding technology definition, three main advantages of rototational molding and six steps of rotomolding process, etc.
Rotational molding is known as rotomolding, plastic rotational casting, roto-molding or rotomold. Rotational molding is a specialized molding process for manufacturing one-piece, hollow plastic parts. The process uses the principles of centrifugal force to move molten stock up against the inside surfaces of a rotating mold and leaving the central part hollow. It is a very competitive alternative to Blow Moulding, Thermoforming and Injection Moulding for the manufacture of hollow plastic parts.
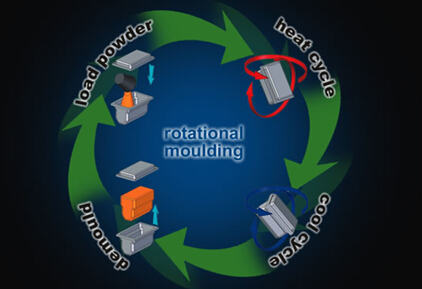 There are six steps in the rotomolding process:
There are six steps in the rotomolding process:
1. Weighing the polyethylene powder. The mold or cavity is filled with a predetermined amount of polyethylene powder. This is called “charging the mold.”
2. The mold halves are secured together by a series of bolts or clamps. For totally enclosed pieces, the entire mold is made of heat conductive metal. When one or both ends of the piece are open, heat-insulating covers are used to close the mold.
3. The charged mold is placed in an oven where it is heated and simultaneously rotated around two axes in planes at right angles to each other.
4. During the heating/rotation cycle the resin melts, fuses and then takes on the shape of the mold being used to form the hollow object.
5. When all the powder has fused into a homogenous layer on the walls of the mold cavity, a combination of air and water is used in a cooling chamber to cool the mold slowly. This helps maintain the part’s dimensional stability.
6. The molds are removed from the cooling chamber, opened and the finished parts removed. The mold is then readied for the next cycle. Before the molds are recharged and steps one through six repeated, it is important to be sure no moisture is on the inside of the mold.
A variety of polymer materials can be used to provide specific characteristics to the products. By using multiple charges, a foaming agent can be added to provide insulating qualities. Close tolerances and tight radii can also be made to allow interchangeable and interlocking component.
If plastics make the world go round, then rotational molding makes the world spin even faster. Rotational molded plastics are an ever-present aspect in our daily life, from catering equipment to portable. Rotational molded plastics are a staple of those products that make our lives easier.
Using plastics rather than metal can contribute to a more durable, long lasting product, meanwhile, they are economical and safety.
It’s a known fact that the more components there are in a part, the greater the risk for breakdowns and problems. Thanks to Rotational moulded technology, the one-part construction resulting in greater durability and longer-lasting products.Plastic parts are extremely impact resistant and do not dent, even stainless steel products are susceptible to rust in welded spots. Plastic parts can also be reinforced with inserts in high-stress areas.
It takes less fuel to operate equipment with plastic parts because plastic is lighter weight than metal. Plastic is typically less expensive than metal. And because rotomolding easily allows for one-piece construction, assembly times – and therefore assembly costs – are reduced.
Rotomolding plastic eliminates sharp corners and burrs and results in a smooth, seamless product. This reduces injury risks for operators. And because rotomolding allows more control over the design, more ergonomic parts can be created.
